To set things straight right off the bat, this article is not generated by any AI nor any natural-language processing system, such as ChatGPT.
It is no secret that cyberthreat actors capitalize on prominent social events latest technology buzzwords to launch their attacks. And the curtain raiser for 2023 that made the headlines was the clamor and viral use of a very human-sounding, artificial technology chatbot named, ChatGPT. A better way to understand what ChatGPT is and what it does in a nutshell is to ask itself:
Given its breakthrough in practical use and public availability, there were growing fears of its possible misuse, social and cyber security implications, which are best described from our earlier article entitled, ChatGPT: What AI holds in store for security. One of the front-page stories in social media and news recently, was the possibility of converting ChatGPT into its devil-may-care alter ego called DAN for “Do Anything Now” in order to produce offensive responses to wide range of sensitive topics. However, just in the second week of February, G DATA Malware Analysts were able to identify a real evil twin of ChatGPT – chatgpt-go.online.
Validate its Looks – Dissecting the Web interFACES
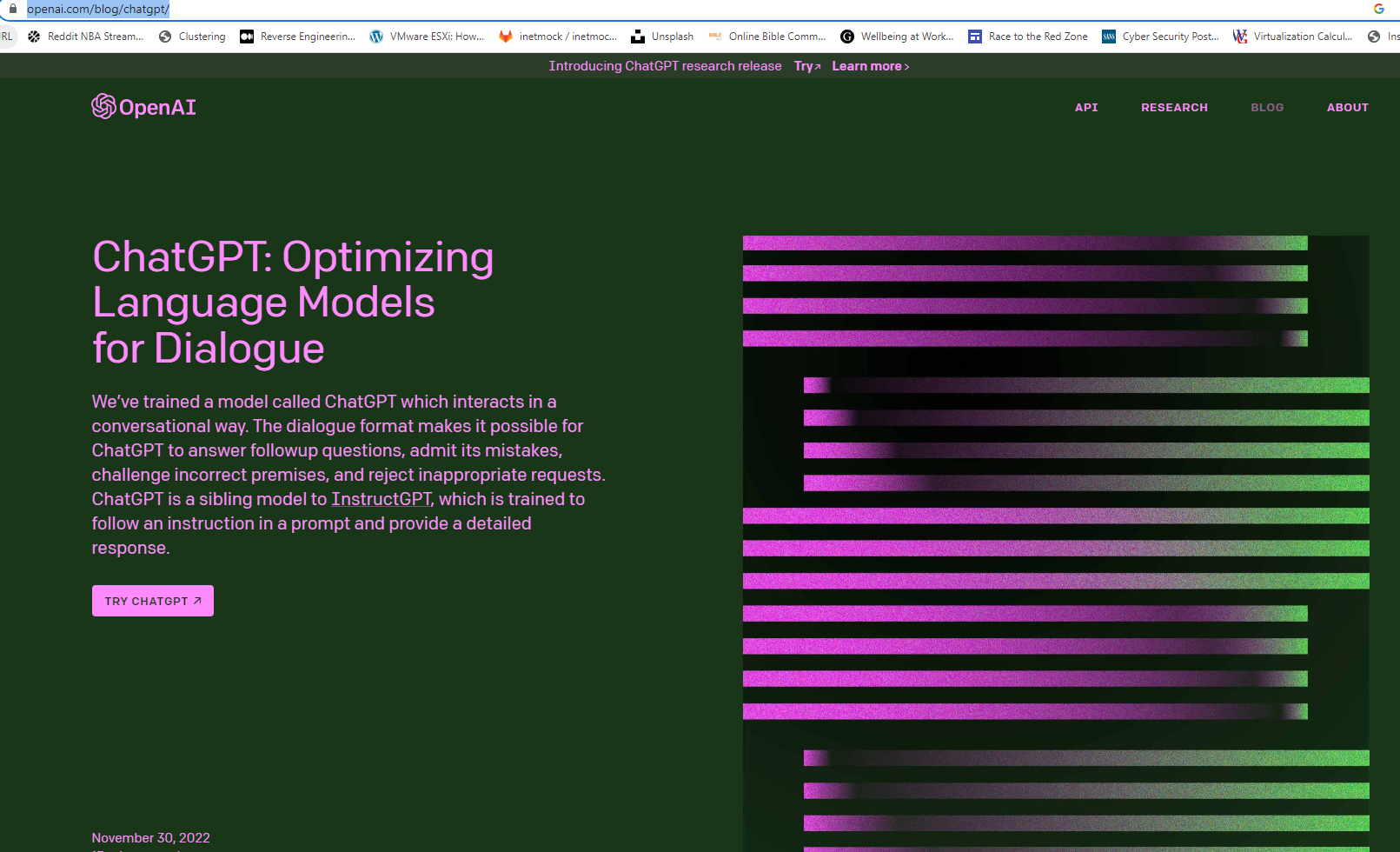
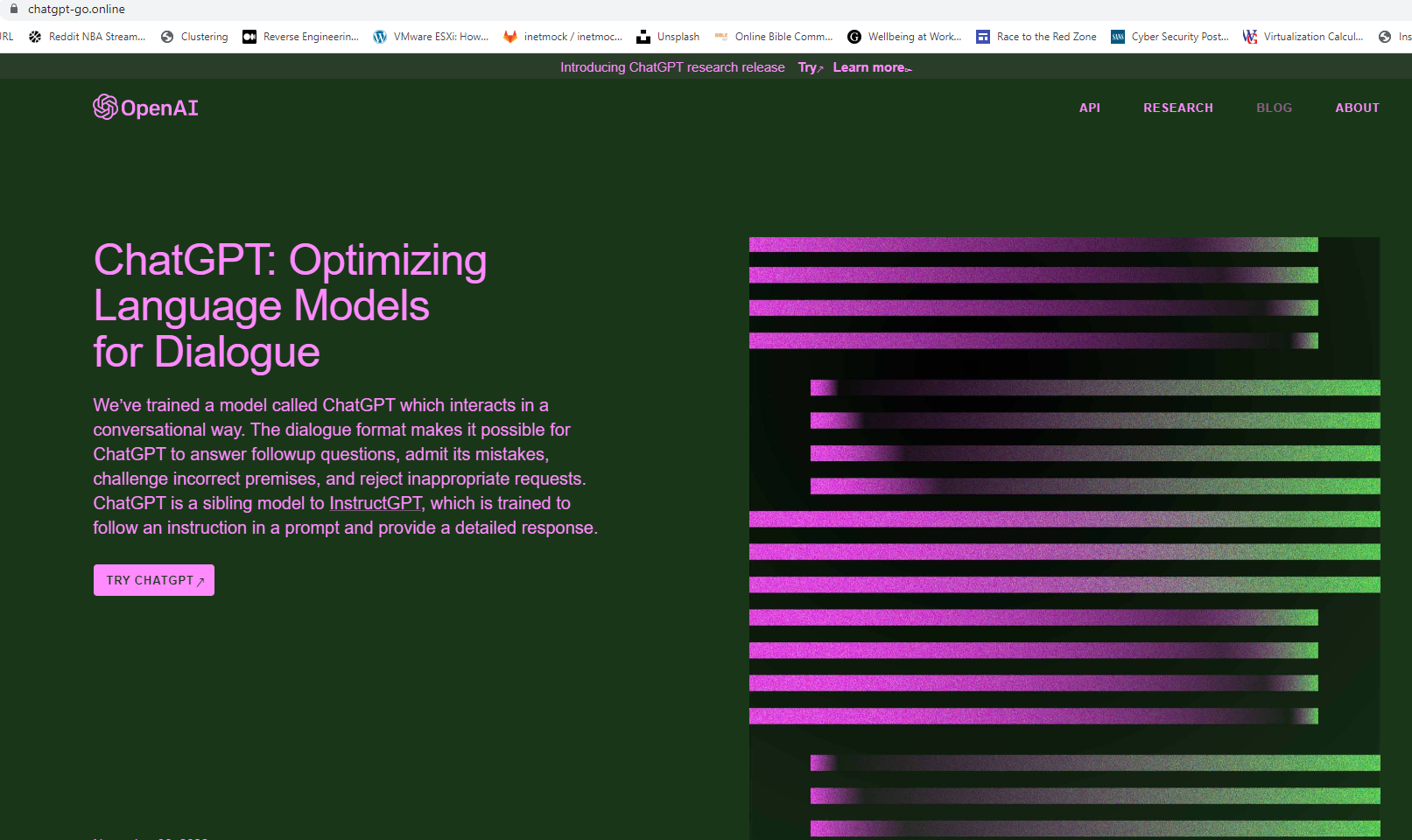
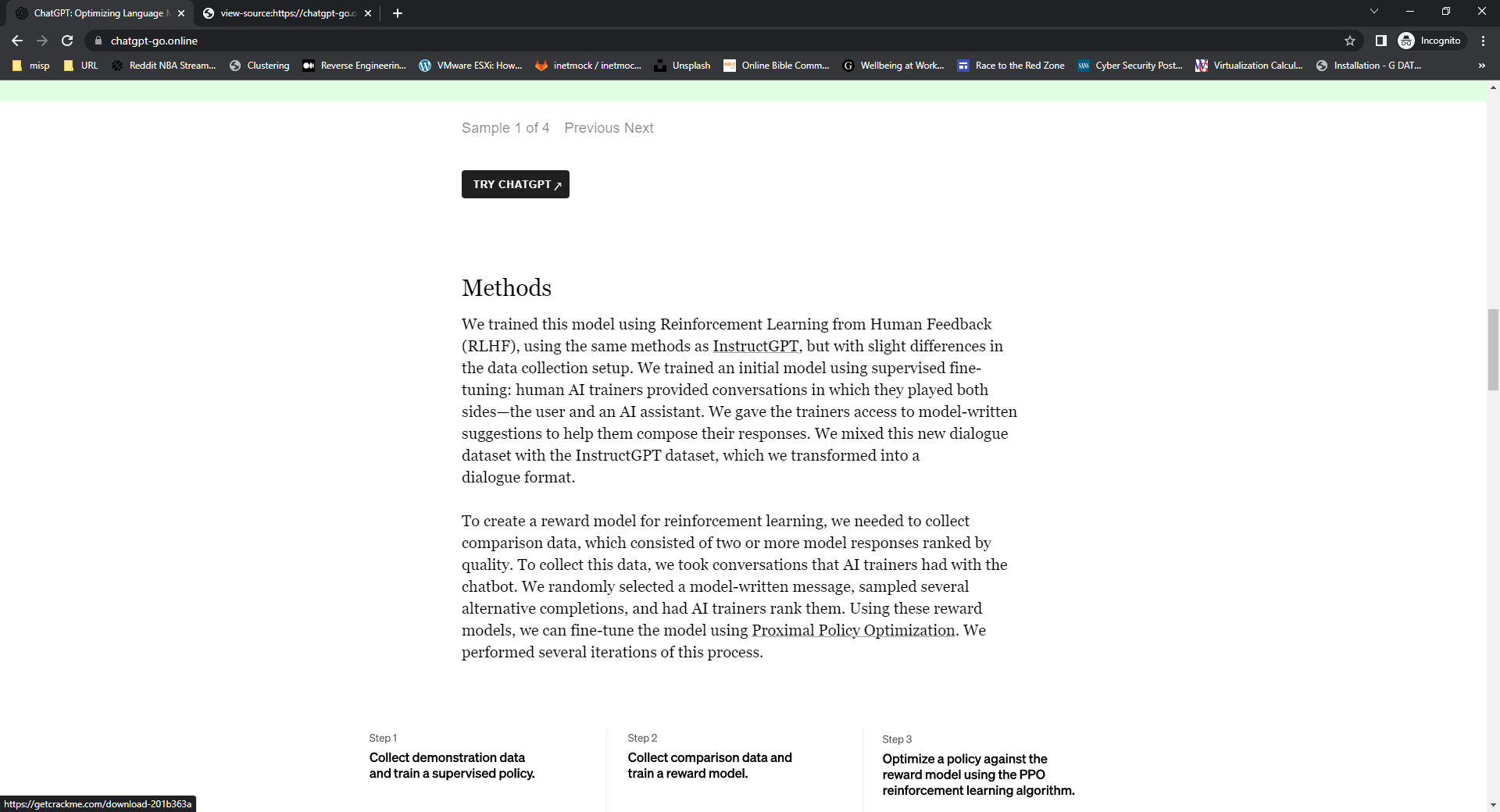
The real webpage of ChatGPT is accessed via openai.com/blog/chatgpt/ , wherein users will be able to experience chatting with the AI is by clicking the TRY CHATPT button that redirects to a Login and Sign Up page. But when users access the fake website, you will be shown the same webpage of the authentic ChatGPT page. It even made use of HTTPS to host its website to convince site visitors its legitimacy by having a secured communication through private and encrypted data traffic between the users’ web browser and the website’s server. That is why not every website using HTTPS is automatically secured and safe to use.
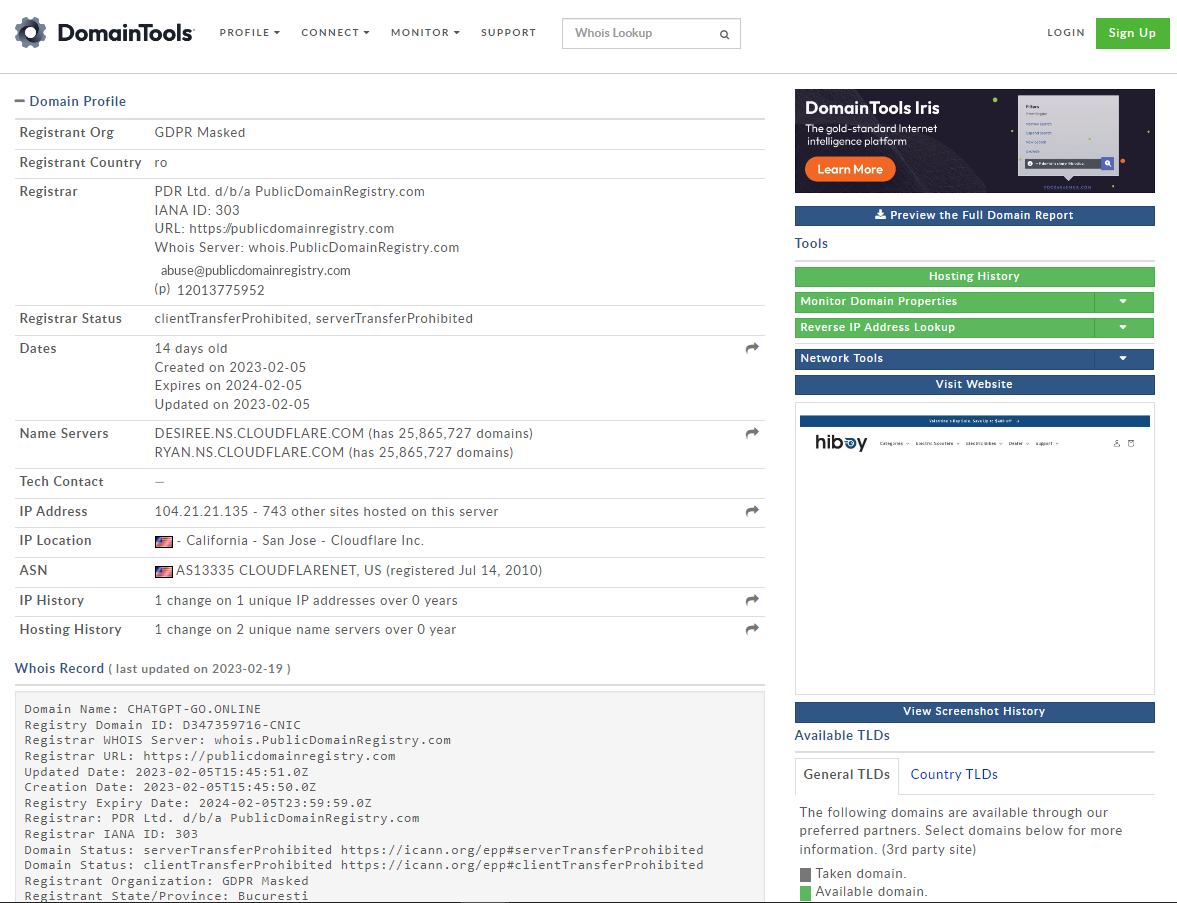
One way of checking a website’s credibility is to validate its “birthdate” – when it was registered and went online. In chatgpt-go.online’s case, it was just four-weeks old at the time of this writing, which raises a flag since ChatGPT had been around since late November of 2022. What raised the curiosity of our Malware Analysts was to see how the fake webpage does its next trickery, whether does it have its own AI chatbot or offers anything else. Lo and behold, it used a classic technique of drive-by download, wherein when the user clicked the TRY CHATGPT button, it will download a malicious file, Installer_3.64_win64_86-setup+manual.zip hosted from hxxps://getcrackme.com/.
What raised the curiosity of our Malware Analysts was to see how the fake webpage does its next trickery, whether does it have its own AI chatbot or offers anything else. Lo and behold, it used a classic technique of drive-by download, wherein when the user clicked the TRY CHATGPT button, it will download a malicious file, Installer_3.64_win64_86-setup+manual.zip hosted from hxxps://getcrackme.com/.
The malware poses as a normal installer of a non-specific software that is copyrighted by Electron and Github, and digitally signed by TeamViewer Germany. It arrives in the system in a package along with usual, normal file components of an installer such as LICENSE, language resources, library, and among others as part of its pretension.
Looking at the image above, the malware's file size is around 700 MB. If a user does not have any idea about the file, he may really think that the file is just a normal installer. But inspecting it further using a static analysis tool called Hiew (Hacker’s View), the actual size of the malware is just around 5 MB only, as the remaining contents of the file are padded with null bytes as shown in the image below. File bloating is a typical approach that malware authors use to evade antivirus detection.
This malware is one of the many advertised malwares called LummaC2 stealer which gathers sensitive information from the affected system. To make it difficult for Malware Analysts from to reverse engineer and understand its behavior, this file is protected with VMProtect v.3.6.0 - 3.7.3.
It gathers the following information from the compromised computer and saves it in a text file named as system.txt:
- HWID
- Screen Resoluton
- Language
- CPU Name
- Physical Installed Memory
It then specifically targets the following applications by gathering information such as user profiles, server information and its credentials:
- AnyDesk
- FileZilla
- KeePass
- Steam
- Telegram
It also steals user information from the following internet browsers through its user data directory:
- Chrome
- Chromium
- Edge
- Kometa
- Opera Stable
- Opera GX Stable
- Opera Neon
- Brave Software
- Comodo
- CocCoc
Moreover, it tries to steal user accounts from two-factor authentication and password manager applications via browser extensions:
- bhghoamapcdpbohphigoooaddinpkbai - Authenticator
- gaedmjdfmmahhbjefcbgaolhhanlaolb - Authy
- oeljdldpnmdbchonielidgobddffflal - EOS Authenticator
- ilgcnhelpchnceeipipijaljkblbcobl - GAuth Authenticator
Extension ID and Password Manager
- imloifkgjagghnncjkhggdhalmcnfklk - Trezor Password Manager
To immediately achieve financial gain, the malware steals numerous cryptocurrency wallets via browser extension IDs as enumerated in the table below.The malware also creates a list of the installed applications in the system and saves it in a text file named as software.txt. It also captures a screenshot of the affected system then saves it as screen.png.
After all these pieces of information are gathered, they will be sent to the malware’s command and control (C&C) server, 77.73.134.68, which is still up and running as of this writing. The figures below show such communication between the affected system and server.
According to VirusTotal’s Threat Intelligence report, this archive file has been seen across different continents from, Asia, Latin America and Europe being the most at 73% that include Germany.
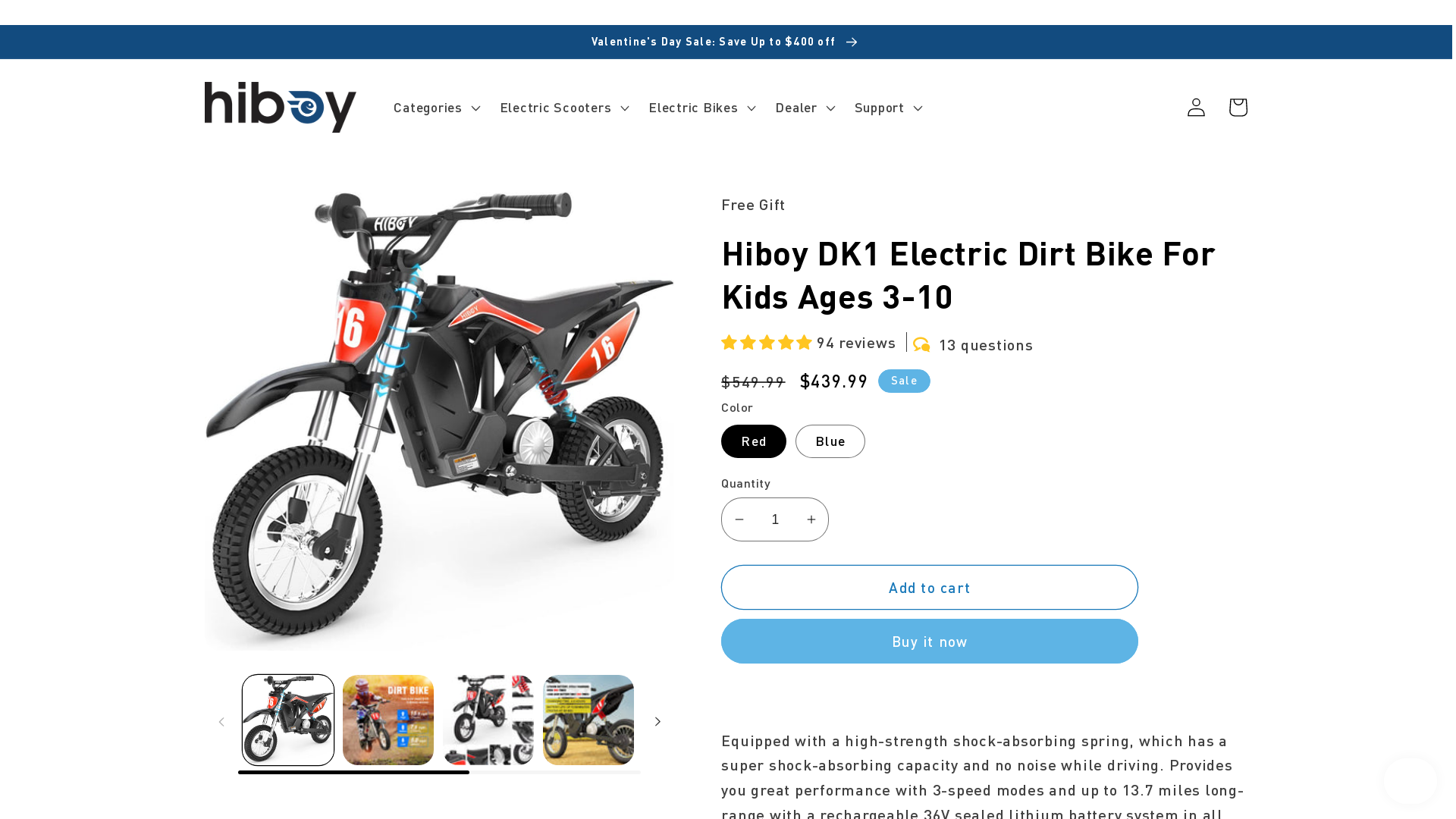
Another interesting feature of this website is when the Malware Analysts tried to access it via Tor, it was dynamic as it served a different web page, which is an e-commerce site directly taken away from Hiboy e-Bike web store. This method is called Shared IP Hosting that is legitimate in its nature, but leveraged by threat actors to conceal mischievous behavior of certain sites.
But wait - there’s more…
Being a fake ChatGPT website is just a façade of this threat, as G DATA Malware Analysts were able to gather from the organization’s internal telemetry and intelligence that the website is also a home of two malicious files with similar intent.
The first file that we were able to source is hosted directly from the fake ChatGPT site, which has the filename Clip.exe. It is a clipboard banker malware that captures user data and cryptocurrencies through Windows clipboard. The infected system though must have an updated Universal C runtime installed as part of the module dependencies of the malware. It targets wallet addresses of different crypto currencies by using regular expressions which are provided in the table below.
The next file that we were able to obtain again directly from the fake ChatGPT site is Java.exe. In a nutshell, it is similar to the two previous malwares, which takes the screenshot of the affected system, and steals from numerous cryptocurrency wallets from the infected host. The file attempts to establish a connection to 194.87.71.146 via port 8081, but it was unsuccessful. It is most likely linked to Aurora stealer, a current prevalent malware family sold on Telegram and underground forums, due to the similarity of its behavior in terms of fingerprinting the affected system and the targeted cryptocurrency wallets.
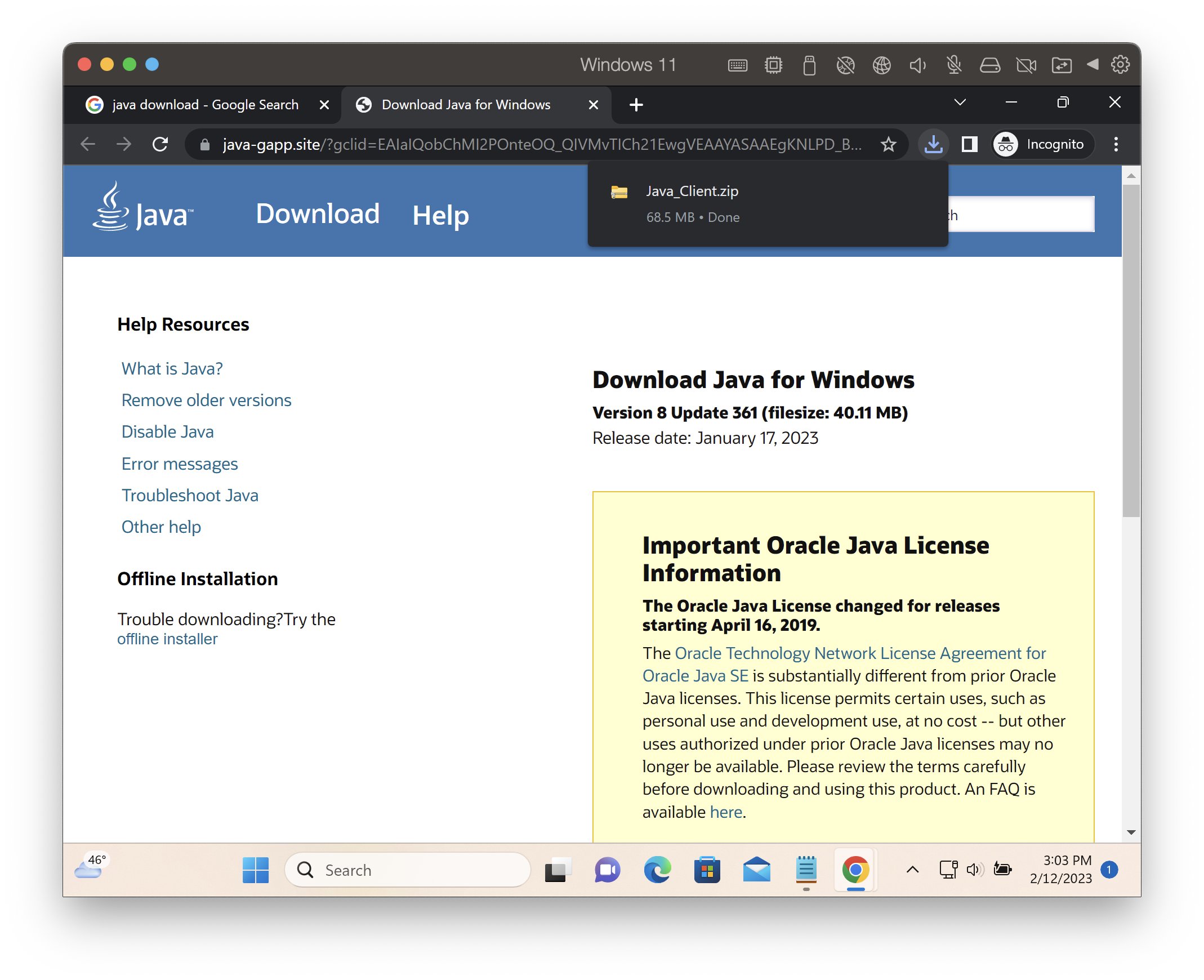
These information and facts gave us the impression that this could be a part of a bigger scheme or cyberthreat campaign. Fellow cybersecurity researcher, Will Dormann had an insight and proof on this, as users will actually be exposed to these threats by just casually searching for legitimate applications via Google, wherein the sponsored Ads on the initial search results were the malicious links. In his investigation, he searched for Java installer in Google, then the top most result is an sponsored paid ad, which actually directs the user to a fake Java website. When the user then selected to download the Java installer, it will then be directed to the fake ChatGPT hosted malware, Java.exe.
G DATA Malware Analysts tried to replicate the possible vector, but Google has already suspended its sponsored ad results and may possibly doing its own investigation and cleanup of its famed service. So please standby for updates on this developing threat as we try to further unravel the end-to-end campaign.
IOC list and information for fellow researchers
SHA256 | Filename – File Type | G DATA Detection |
46200951190736e19be7bcc9c0f97316628acce43fcf5b370faa450e74c5921e | Clip.exe (PE32) | ClipBanker39 |
34b88f680f93385494129bfe3188ce7a0f5934abed4bf6b8e9e78cf491b53727 | Java.exe (PE32) | AuroraStealer |
2ac5138fafdb2b9919907469da051a8bd65bbfb7bce71078b38b6be8dcc8ca18 | Installer_3.64_win64_86.exe (PE32) | LummaStealer3; CoinStealer14 |
URL | Description |
chatgpt-go.online | Fake ChatGPT URL |
77.73.134.68 | LummaStealer’s C&C server |
Targeted Cryptocurrency wallets | Extension IDs/ Path/Regular Expression |
SHA256: 2ac5138fafdb2b9919907469da051a8bd65bbfb7bce71078b38b6be8dcc8ca18 | |
MetaMask | nkbihfbeogaeaoehlefnkodbefgpgknn |
MetaMask (Edge) | ejbalbakoplchlghecdalmeeeajnimhm |
TronLink | ibnejdfjmmkpcnlpebklmnkoeoihofec |
Ronin | fnjhmkhhmkbjkkabndcnnogagogbneec |
Binance | fhbohimaelbohpjbbldcngcnapndodjp |
Yoroi | ffnbelfdoeiohenkjibnmadjiehjhajb |
Nifty | jbdaocneiiinmjbjlgalhcelgbejmnid |
Math | afbcbjpbpfadlkmhmclhkeeodmamcflc |
Coinbase | hnfanknocfeofbddgcijnmhnfnkdnaad |
Guard | hpglfhgfnhbgpjdenjgmdgoeiappafln |
Equal | blnieiiffboillknjnepogjhkgnoapac |
Jaxx Liberty | cjelfplplebdjjenllpjcblmjkfcffne |
BitApp | fihkakfobkmkjojpchpfgcmhfjnmnfpi |
iWallet | kncchdigobghenbbaddojjnnaogfppfj |
Wombat | amkmjjmmflddogmhpjloimipbofnfjih |
MEW CX | nlbmnnijcnlegkjjpcfjclmcfggfefdm |
Guild | nanjmdknhkinifnkgdcggcfnhdaammmj |
Saturn | nkddgncdjgjfcddamfgcmfnlhccnimig |
Liquality | kpfopkelmapcoipemfendmdcghnegimn |
Terra Station | aiifbnbfobpmeekipheeijimdpnlpgpp |
Enkrypt | kkpllkodjeloidieedojogacfhpaihoh |
NeoLine | cphhlgmgameodnhkjdmkpanlelnlohao |
CLV | nhnkbkgjikgcigadomkphalanndcapjk |
Keplr | dmkamcknogkgcdfhhbddcghachkejeap |
Sollet | fhmfendgdocmcbmfikdcogofphimnkno |
Auro | cnmamaachppnkjgnildpdmkaakejnhae |
Polymesh | jojhfeoedkpkglbfimdfabpdfjaoolaf |
ICONex | flpiciilemghbmfalicajoolhkkenfel |
Nabox | nknhiehlklippafakaeklbeglecifhad |
KHC | hcflpincpppdclinealmandijcmnkbgn |
Temple | ookjlbkiijinhpmnjffcofjonbfbgaoc |
TezBox | mnfifefkajgofkcjkemidiaecocnkjeh |
DAppPlay | lodccjjbdhfakaekdiahmedfbieldgik |
BitClip | ijmpgkjfkbfhoebgogflfebnmejmfbml |
Steem Keychain | lkcjlnjfpbikmcmbachjpdbijejflpcm |
Nash | onofpnbbkehpmmoabgpcpmigafmmnjhl |
Hycon Lite | bcopgchhojmggmffilplmbdicgaihlkp |
ZilPay | klnaejjgbibmhlephnhpmaofohgkpgkd |
Coin98 | aeachknmefphepccionboohckonoeemg |
Cyano | dkdedlpgdmmkkfjabffeganieamfklkm |
Byone | nlgbhdfgdhgbiamfdfmbikcdghidoadd |
OneKey Legacy | infeboajgfhgbjpjbeppbkgnabfdkdaf |
LeafWallet | cihmoadaighcejopammfbmddcmdekcje |
Binance | %appdata%\Binance |
Electrum | %appdata%\Electrum\wallets |
Ethereum | %appdata%\Ethereum\keystore |
Exodus | %appdata%\Exodus |
Ledger Live | %appdata%\Ledger Live |
Atomic | %appdata%\atomic\Local Storage |
Coinomi | %localappdata%\Coinomi\Coinomi\wallets |
Steam | %programfiles%\Steam |
|
|
SHA256: 34b88f680f93385494129bfe3188ce7a0f5934abed4bf6b8e9e78cf491b53727 | |
Coin98 | aeachknmefphepccionboohckonoeemg |
Terra Station | aiifbnbfobpmeekipheeijimdpnlpgpp |
Wombat | amkmjjmmflddogmhpjloimipbofnfjih |
BOLT X | aodkkagnadcbobfpggfnjeongemjbjca |
Phantom | bfnaelmomeimhlpmgjnjophhpkkoljpa |
Equal | blnieiiffboillknjnepogjhkgnoapac |
EVER | cgeeodpfagjceefieflmdfphplkenlfk |
Jaxx Liberty | cjelfplplebdjjenllpjcblmjkfcffne |
Maiar DeFi | dngmlblcodfobpdpecaadgfbcggfjfnm |
Yoroi | ffnbelfdoeiohenkjibnmadjiehjhajb |
Binance | fhbohimaelbohpjbbldcngcnapndodjp |
Oxygen | fhilaheimglignddkjgofkcbgekhenbh |
BitApp | fihkakfobkmkjojpchpfgcmhfjnmnfpi |
Ronin | fnjhmkhhmkbjkkabndcnnogagogbneec |
Harmony | fnnegphlobjdpkhecapkijjdkgcjhkib |
XDEFI | hmeobnfnfcmdkdcmlblgagmfpfboieaf |
Coinbase | hnfanknocfeofbddgcijnmhnfnkdnaad |
Guard | hpglfhgfnhbgpjdenjgmdgoeiappafln |
TronLink | ibnejdfjmmkpcnlpebklmnkoeoihofec |
Nifty | jbdaocneiiinmjbjlgalhcelgbejmnid |
iWallet | kncchdigobghenbbaddojjnnaogfppfj |
Liquality | kpfopkelmapcoipemfendmdcghnegimn |
Nami | lpfcbjknijpeeillifnkikgncikgfhdo |
Atomic | AppData\Roaming\atomic\Local Storage\leveldb |
Armory | AppData\Roaming\Armory |
Electrum | AppData\Roaming\Electrum\wallets |
Ethereum | AppData\Roaming\Ethereum\keystore |
Exodus | AppData\Roaming\Exodus\exodus.wallet |
Jaxx Liberty | AppData\Roaming\com.liberty.jaxx |
Guarda | AppData\Roaming\Guarda\Local Storage\leveldb |
|
|
SHA256: 46200951190736e19be7bcc9c0f97316628acce43fcf5b370faa450e74c5921e | |
Bitcoin | ^(bc1|[13])[a-zA-HJ-NP-Z0-9]{25,39}$ |
USDT-TRON | T[A-Za-z1-9]{33} |
Ethereum | ^0x[a-fA-F0-9]{40}$ |
LiteCoin | ^([LM3]{1}[a-km-zA-HJ-NP-Z1-9]{26,33}||ltc1[a-z0-9]{39,59})$ |
XRP | r[0-9a-zA-Z]{24,34} |
Doge | D{1}[5-9A-HJ-NP-U]{1}[1-9A-HJ-NP-Za-km-z]{32} |
Monero | [48][0-9AB][1-9A-HJ-NP-Za-km-z]{93} |